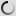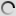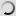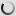Takin – Budorcas taxicolor
Takin – Budorcas taxicolor
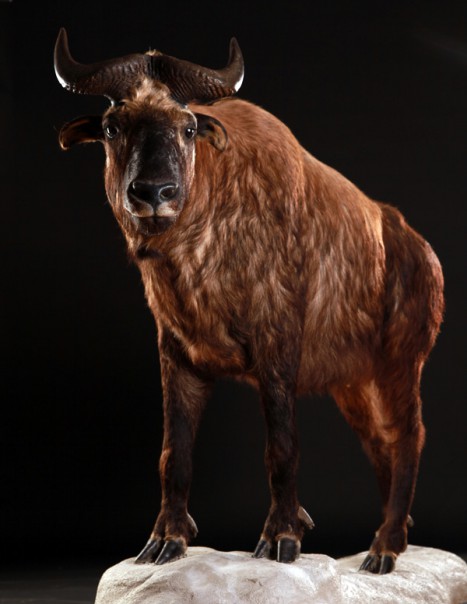
The takin is a bovid that particularly appreciates the high mountain areas. This animal can measure up to 130 cm tall and can weigh up to 350 kg. The takin lives in the mountainous regions of Asia. Their habitat is mostly located between 2.000 and 4.500 meters altitude. A large number of individuals is recorded in Bhutan, China, India and Myanmar.
This animal lives in small groups. A group can be up to 100 individuals at the coldest time of winter.
Sexual maturity of the female takin is reached after two to two and half years. Mating can be done during the summer seasons. The gestation period of takin is about 8 months. The female gives birth to only one child. After birth, the small weaned at the age of 9 months.
Herbivore, takin feeds mainly of grass, leaves and twigs. Young bamboo shoots are also a food of choice for the takin. The takin particularly appreciates the salt. It is for this reason that the animal does not hesitate to lick long the rocks.
Despite its imposing appearance, the takin is a timid animal. In case of danger, it can run quickly and with agility to cross the obstacles presented by the rugged ground of the mountain. When running, takin always charges head down. The warning signal of this animal looks like a cough. This same sound, but a bit more serious also serves to attract females during rutting season. To mate with a female, the males sometimes engage in a fight to death.
During the summer, takin group always travels together. The herd is made up of ten to a hundred individuals. When food is running out, especially during the winter, the group disperses to meet again with the approach of the season of love. The life of a takin is about fifteen years.
Apart from natural predators, the takin is disappearing largely because of humans. The Chinese are indeed fond of the flesh of the takin.