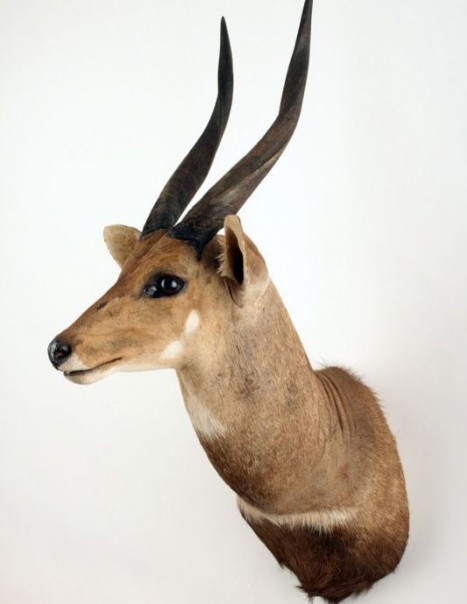
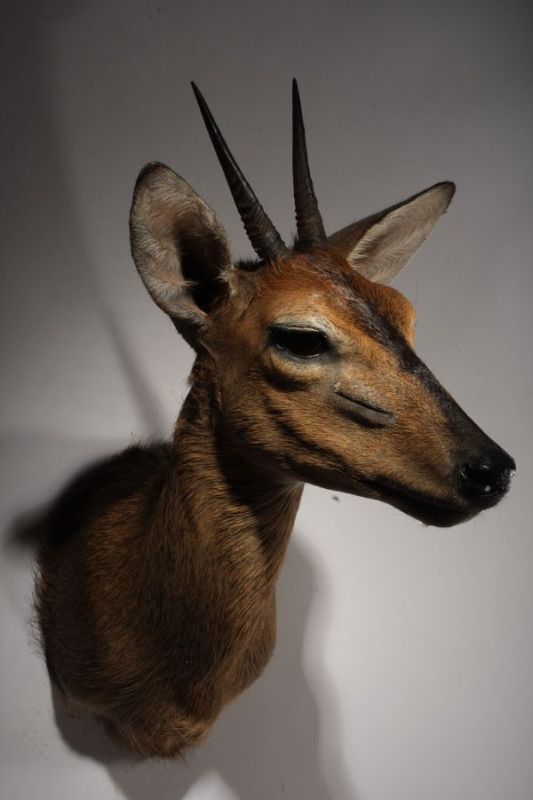
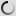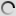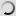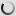Bushbuck – Shoulder mount/stuffed head – Tragelaphus scriptus
Bushbuck – Tragelaphus scriptus
The bushbuck, also called Guib, is an antelope of the Bovidae Bovinae family.
The Guib lives in much of sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in Zimbabwe, Botswana and northern Namibia. We meet it in a habitat where the vegetation is either open or closed, provided that a permanent water source is nearby. The Guib is located in territories of elevations below 3000 meters.
The Guib is a cétartiodactyle, it means that the mammal have an even number of fingers. Its coat is reddish-brown white mottled, the dress of the female is more vivid. A black line runs through the muzzle and a white spot is observed on each of its cheeks. The male also has two twisted horns. The Guib measures between 1 m and 1.50 m long and between 60cm and 1m at the withers. The male, which weighs between 30 and 80kg, is more stouts than the female, weighing between 20 and 60kg.
This herbivore ruminant feeds mainly on leaves, grass pea crop, shoots and roots. It is also common that it follows baboons and other monkeys to pick the fruit that they would fall.
Nature shy and lonely, it can still be very brave: it is not afraid to fight predators. Bushbuck live in pairs or in small family groups. The hierarchy between males is determined by age.
The Guib is a placental mammal. It reaches sexual maturity at the age of one and a half year. Females have one litter a year, which, in general, gives birth to a little after six months of pregnancy. Male offspring will remain with the mother until the appearance of the horns and young females will accompany it to the next calving.
The lifetime of the animal is estimated at 12 years at most.
According to the IUCN, the concern is only minor on its conservation: the species is not threatened.