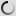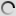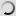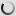Chinese bamboo partridge – Bambusicola thoracicus
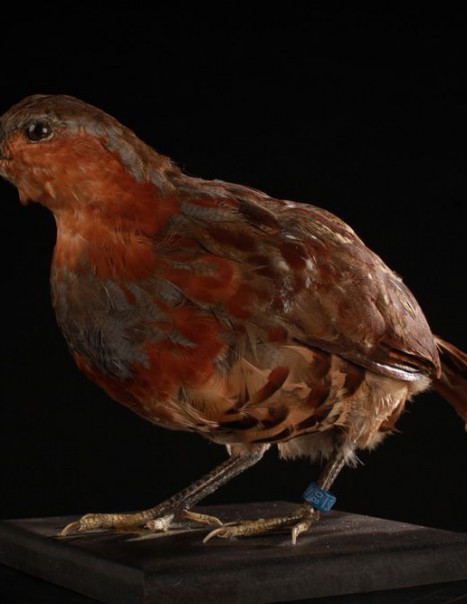
Chinese bamboo partridge – Bambusicola thoracicus
The Bambusicola thoracicus is a species of bird of the family Phasianidae.
Originally from the South China: Sze-Chuan, Hunan, Fukien, Kiangsi, southern Chekiang and Taiwan. This species has also been introduced in Japan successfully.
In Taiwan this partridge is darker, flanks spots are hazel, not black. The gray breast band is wider. This Partridge frequents grassy expanses, interspersed with thickets and bamboo clumps to 1000 m above sea level, sometimes a little higher, up to 2000m.
In Taiwan, the partridge is changing in places more or less disturbed in crops, tea plantations, along roadsides and even clumps of bamboos located near hotels and private residences.
The Chinese bamboo partridge lives with companies ranging from 2 to 20 territorial birds, it is active in the early morning.
Its diet includes seeds, shoots, leaves and invertebrates collected in crops and fallow land, sometimes in domestic poultry company. This species is common to a wide range which puts it in the shelter of a direct threat.
Declines in populations are important because of habitat destruction and overhunting. However, the population would be stable in Taiwan.
It is likely that this species is monogamous but to date, no study has been conducted on this subject. The groups are dispersed in the spring, the males become aggressive and the nest is then placed in a thicket, a clump of bamboo or foot of a tree, just in a clump of grass. This partridge is easily approached and up at the last moment, scattering in all directions. Its territorial call is powerful, birds meet in a duo.
Outside the breeding season, the song is more harmonious.