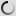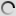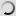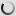Chimpanzee – Pan troglodytes
Chimpanzee – Pan troglodytes
The chimpanzee or an anthropoid Chimpanzee is native to equatorial Africa.
According to the classification, the chimpanzee is part of the Animal Kingdom, the class of mammals, Order Primates, Family of Hominidae and pan gender. The common chimpanzee is mainly found in Sierra Leone, Victoria and Lake Tanganyika. Essentially encounter the dwarf chimpanzee or bonobo in the Congo River basin. It is a large diurnal arboreal monkey. Indeed, its body with disproportionate arm allows it to climb or swing on trees.
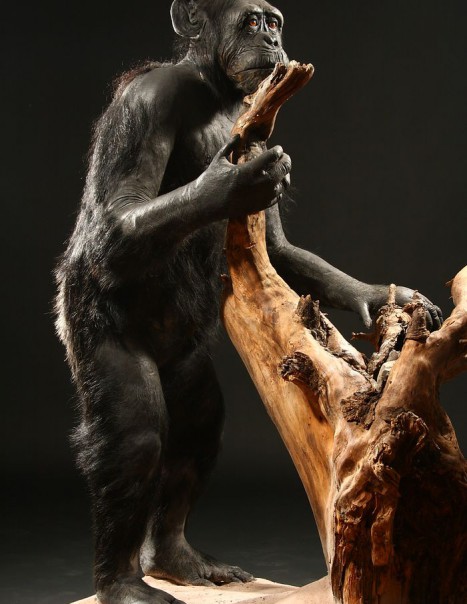
Genetically, the chimpanzee is the animal that is closest to humans. Moreover, its face, the palms of its hands and the soles of its feet are hairless.
The animal is similar to the appearance of a human with a height up to 170 cm for males and 130 cm for females. The weight of adults ranges from 45 kg to 80 kg and can live up to 45 years.
The chimpanzee has a body covered with a uniform dark coat and it has no tail. It has long arms whose length corresponds to one and a half times the height of his body. It has short toes and wide soles of feet which explains its adaptation to walking. At its head, the eyebrows, lips and ears are prominent.
The chimpanzee is omnivorous but its feeding is frugivorous dominance. However, it also feeds on flowers, seeds, honey and insects.
Gestation lasts between 202 and 261 days and in general gives birth to a single baby. The average interval between births is three years. The female chimpanzee gives birth for the first time at the age of 13 years although it reached puberty early at the age of 7 years.
Depending on the status of IUCN, the chimpanzee is critically endangered due to habitat destruction and hunting in its native range.