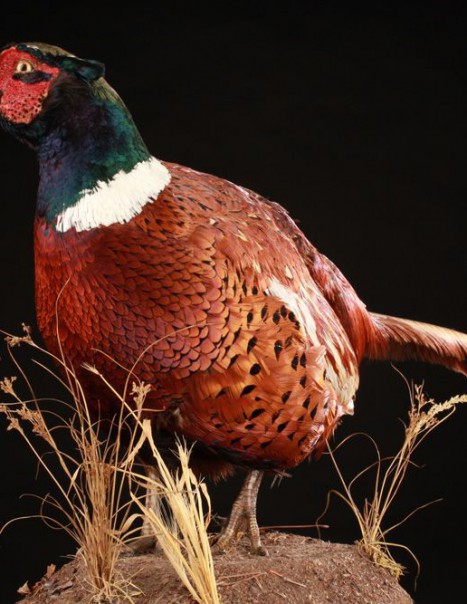
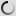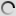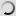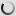Common Pheasant – Phasianus colchicus
Phasianus colchicus – Common pheasant
The common pheasant belongs to the pheasant family – Phasianidae.
It is native of Asia and has been widely introduced elsewhere as a game bird.
There are many colour forms of the male common pheasant, ranging in colour from nearly white to almost black in some melanistic examples. These are due to captive breeding and hybridation between subspecies and with the green pheasant, reinforced by continual releases of stock from varying sources to the wild.
There are about 30 subspecies split in five groups (sometimes six). These can be identified according to the male plumage, namely presence or absence of a white neck-ring and the color of the uppertail (rump) and wing coverts.
In principle, they reach sexual maturity during the second year. The male is polygamous. During the breeding season, pheasants remain in small groups of a rooster and 2 to 5 hens. Within each group, the rooster has a dominant position. The clutch size varies from 6 to 15 eggs. The incubation period does not exceed 27 days. When females incubate, the male stays around them and watch over them.
The common pheasant is omnivorous and has a particularly varied diet, fruits, seeds, berries, buds, young leaves, shoots, bulbs, tubers, insects, earthworms, slugs and small reptiles.